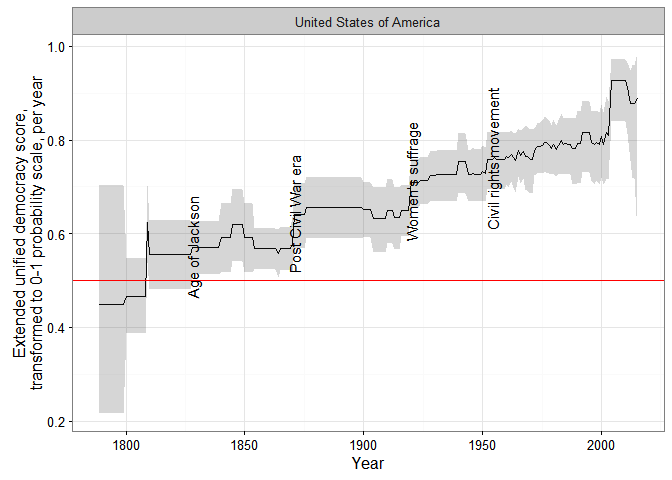
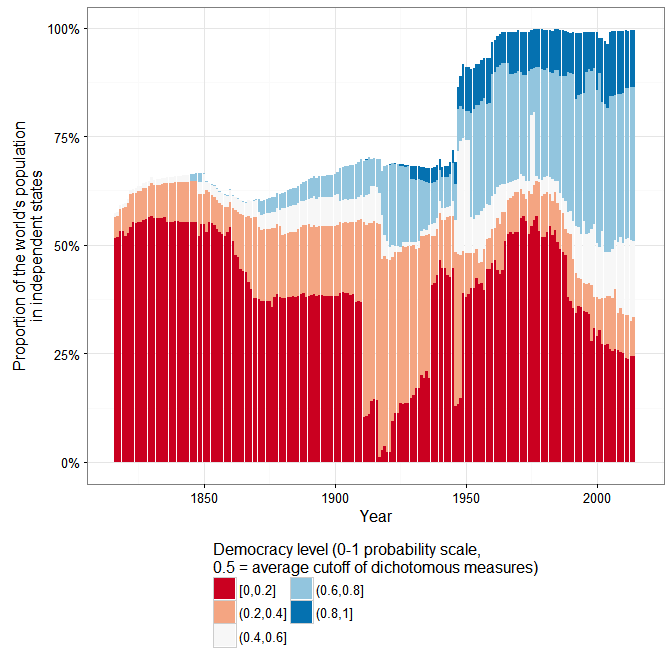
I recently finished Nina Tumarkin’s fantastic book
Lenin Lives! The Lenin Cult in Soviet Russia, which is totally up my alley, as you may imagine. (Why hadn’t I heard of this book before? It’s so good!). One really interesting point that comes up in her book is the development, alongside the actual rituals of the cult, of what we might call a “theory of representation” to justify a phenomenon (Lenin worship) that was
prima facie contrary to the tenets of Marxism (and even to Lenin’s own wishes). And it struck me that this spontaneously developed and unsystematic “political theology” (to use a more pretentious term) was strikingly similar to the medieval doctrine of “
the King’s two bodies.”
The idea of the King’s two bodies is in principle quite simple: the King’s authority does not come from any of his actual personal qualities, but from his personification of the “body politic,” to which his natural body is joined. Kantorowicz (in a
famous book) traces this view to its roots in the relationship between the incarnate body of Christ and the Church as a “body” of believers, though this is not particularly important for our purposes here. A passage from
Plowden’s Reports gives the gist of the view as it was understood by the jurists and lawyers of the Tudor period:
For the King has in him two Bodies, viz., a Body natural, and a Body politic. His Body natural (if it be considered in itself) is a Body mortal, subject to all Infirmities that come by Nature or Accident, to the Imbecility of Infancy or old Age, and to the like Defects that happen to the natural Bodies of other People. But his Body politic is a Body that cannot be seen or handled, consisting of Policy and Government, and constituted for the Direction of the People, and the Management of the public weal, and this Body is utterly void of Infancy, and old Age, and other natural Defects and Imbecilities, which the Body natural is subject to, and for this Cause, what the King does in his Body politic, cannot be invalidated or frustrated by any Disability in his natural Body (p. 7)
We might say that the king “represents” the state (makes it present) by personifying it physically; despite the fact that Louis XIV never actually said “L’Etat, c’est moi,” it is the sort of thing that would have made sense for him to say, as it summarizes this view quite well. And in personifying the state, the king’s “natural body” is in a sense “
wiped clean,” gaining a kind of grace (“charisma”). To use Max Weber’s terminology, the “charismatic authority” of the king – his authority in virtue of the kind of person he is – thus becomes “routinized” , no longer dependent on his actual personal qualities but merely on his possession of an office. Yet it still remains a form of
personal authority: loyalty and obedience is owed to the actual person of the king, not simply or solely to the abstract body of laws, the state, or the constitution, and the body of the king has a special majesty that must be honored.
Now, the early Bolsheviks would certainly have thought this was all nonsense. Yet the circumstances of the revolution, and in particular the obvious appeal of “charismatic” justifications for authority, seem to have forced them to try to accommodate such claims in ways that ended up being structurally quite similar.
The early Bolsheviks were rather “voluntaristic” by Marxist standards: they did not believe in merely sitting still and waiting for the dialectic of history to work its revolutionary magic. Yet most of them were wary of “heroes,” good Marxists that they were (unlike, say, the members of the
Socialist Revolutionary party). Lenin’s
What is to be Done exalted the role of the vanguard party of professional revolutionaries in the revolutionary process, not the role of any individual leader. And though his enormous energy, clear tactical judgment, and unshakable faith in the triumph of his vision, generated a form of charisma, as evidenced in a number of testimonies from both friends and enemies, he disliked flattery and did not seem to have consciously exploited his talent for “social hypnotism” to personalize state power.[] Other charismatic Bolsheviks (Trotsky, for example) also preferred to exalt the party rather than themselves.
Yet soon after the October revolution it became clear that “charismatic” appeals were exceedingly useful in the struggle for the loyalty of the masses. Already in early 1918 the old Bolshevik M. S. Olminsky argued that though “[t]he cult of personality contradicts the whole spirit of Marxism, the spirit of scientific socialism,” Bolsheviks should not ignore their leaders, who personified the party and the working class (Tumarkin,
p. 87). Individual Bolsheviks – primarily, but not exclusively, top leaders like Lenin – were both
exemplars of the values that a good Communist should have (and thus to be emulated) and
personifications of the proletariat (and thus to be honored). Lenin himself, for all his dislike of flattery, was quite conscious of the power of his image, and grudgingly accepted some of the manifestations of the cult growing around him. As Tumarkin puts it:
Lenin’s passive acceptance of publicity doubtless was partly inspired by his perception of the effectiveness of his image in legitimizing the new regime and in publicizing it. As Lunacharsky once observed, “I think that Lenin, who could not abide the personality cult, who rejected it in every possible way, in later years understood and forgave us” … [Lenin] was not ambivalent about playing the role of exemplar, as he did on May Day 1919 when he had worked in the Kremlin courtyard on the first subbotnik (p. 105) []
The cult of Lenin thus grew inexorably, even in the face of Lenin’s personal resistance, from the perception that the values and aspirations of the Bolshevik party were credibly
embodied in his person. Charismatic claims to authority may have been suspect from a theoretical point of view, but they seem to have worked in practice. Yet in order to account for them the Bolsheviks were forced to insist that the veneration of Lenin and other leaders was acceptable because the leader always symbolized and represented, in a heightened degree, the party and the proletariat; to glorify Lenin was thus not to venerate the “hero”
as such, but the proletariat itself, even though the “mortal” body of Lenin was connected to his “symbolic” body.
Possibly the most striking example of this thesis of “Lenin’s two bodies” appears in a piece written when
Lenin was shot by SR member Fanya Kaplan in August 1918. At the time, Bolshevik journalist
Lev Sosnovsky (who was to become the head of the Central Committee’s Agitprop department in 1920) wrote in
Bednota, a newspaper “aimed at the broad mass of peasant readers” that:
Lenin cannot be killed … Because Lenin is the rising up of the oppressed. Lenin is the fight to the end, to final victory … So long as the proletariat lives – Lenin lives. Of course, we, his students and colleagues, were shaken by the terrible news of the attempt on the life of dear ‘Ilich’, as the communists lovingly call him … A thousand times [we] tried to convince him to take even the most basic security precaurions. But ‘Ilich’ always rejected these pleas. Daily, without any protection, he went to all sorts of gatherings, congresses, meetings (pp. 83-84)
Tumarkin comments that in Sosnovsky’s presentation, “Ilich is the mortal man and Lenin is the immortal leader and universal symbol … The mortal man exposed himself to danger, but Lenin cannot be killed.” Yet this piece is not an isolated case, explainable perhaps by Sosnovsky’s attempt to appeal to peasant readers. The futurist poet
Vladimir Mayakovsky, for example, well aware of the problematic nature of leader cults within Marxist thought, nevertheless justified the veneration of Lenin in terms similar to Sosnovsky’s, writing on the occasion of Lenin’s fiftieth birthday (1920):
I know –
It is not the hero
Who precipitates the flow of revolution.
The story of heroes –
is the nonsense of the intelligentsia!
But who can restrain himself
and not sing
of the glory of Ilich? …
Kindling the lands with fire
everywhere,
where people are imprisoned,
like a bomb
the name
explodes:
Lenin!
Lenin!
Lenin! …
I glorify
in Lenin
world faith
and glorify
my faith (p. 100)
Mayakovsky hits on the crucial point: to glorify Lenin is to glorify the values of
his party
because Lenin represents more than the mere mortal Ilich; he represents, as another writer put it in a piece published on the sixth anniversary of the revolution, “a program and a tactic … a philosophical world view … the ardent hatred of oppression … the rule of pure reason … a limitless enthusiasm for science and technology … the dynamic and the dialectic of the proletariat;” in sum, “Lenin is the one Communist Party of the Red Globe” (
p. 132).
In these last couple of passages, Lenin is glorified primarily as a symbol – of the party, the revolution, and the proletariat. But the physical body still mattered; the embodiment of Lenin as Ilich was not irrelevant to his symbolic effectiveness. As Tumarkin notes, both in 1918 (when Lenin was shot) and in 1923 (when he died) the party press had presented Lenin as a sort of physical superman, surviving physical harm that would have killed a lesser man (p. 171); the natural body of the king, joined to his spiritual body, is no longer an ordinary body. And of course, the significance of Lenin’s natural body emerges most clearly in the fantastically strange decision (from a Marxist point of view) to embalm it and put it on public display after his death.
It is not clear, at least at the time Tumarkin was writing (1980s), how the ultimate decision to embalm was made; she suggests that Stalin was the driving force, since he had insisted that Lenin be buried “in the Russian manner” rather than cremated in the “modern” manner. (Cremation was apparently associated with executed prisoners in Russia, and Stalin seems to have been concerned about the bad symbolic connotations of doing this to Lenin). It certainly seems to have been controversial: Trotsky, Bukharin, and Kamenev all opposed it – Trotsky specifically objecting to turning Lenin into an Orthodox icon. So did Lenin’s secretary, Bonch-Bruevich, and Nadezhda Krupskaia (Lenin’s wife) protested publicly when the decision was revealed. The obvious similarities between the worship of the saints in Orthodox Christianity (whose bodies, if they are truly saintly, are not supposed to decay) and the proposal to mummify and exhibit Lenin’s body must have discomfited many “good Bolsheviks.”
But some of the people involved, like
Leonid Krasin, had belonged to the “God-building” movement within Bolshevism, which we could call the transhumanist wing of the Bolsheviks. (Tumarkin tells some fabulous stories about them – both
Gorky and
Lunacharsky, the latter the first “Commissar of Enlightment” were also affiliated with this current of thought). They believed in the power of science (including Marxism, which they saw as the most important part of science) to eventually to overcome death itself, and saw themselves as consciously engaged in the creation of a new divinity. Krasin even “publicly preached his belief in the [physical] resurrection of the dead” through science, and speculated on the potential of
cryonics to preserve the dead until the time “when one will be able to use the elements of a person’s life to recreate the physical person.” (
Bolshevik EMs!). For them, the “immortalization of Lenin was a true deification of man.”
By showing that they could preserve Lenin’s body from corruption, they also seem to have hoped to create a proper sort of communist Saint, whose undecaying body was due to science rather than to God, and thus to help weaken an Orthodox Christianity widely believed by the population. As one of the people involved in the project (Boris Zbarsky) put it after the embalming:
The Russian Church had claimed that it was a miracle that its saints’ bodies endured and were incorruptible. But we have performed a feat unknown to modern science … We worked four months and we used certain chemicals known to science [though the chemicals remained secret - the lore of embalming was among the arcana imperii in the Soviet Union]. There is nothing miraculous about it (p. 196).
Nevertheless, proponents of embalming (the members of the aptly-named “Immortalization Commission”) still had to justify the decision to skeptical Bolsheviks in terms that clearly distinguished between the veneration of Orthodox Saints and the “new” veneration of Lenin. And the best they could come up with was generally some variation on the theme that the
physical body of Lenin would provide genuine happiness to future generations. (I am reminded here of
Mao’s mangoes). Here’s
Avel Enukidze:
It is obvious that neither we nor our comrades wanted to make out of the remains of Vladimir Ilich any kind of “relic” (moshchi) by means of which we would have been able to popularize or preserve the memory of Vladimir Ilich. With his brilliant writings and revolutionary activities, which he left as a legacy to the entire world revolutionary movement, he immortalized himself enough.
[…]
We wanted to preserve the body of Vladimir Ilich, not in order simply to popularize his name, but we attached and [now] attach enormous importance to the preservation of the physical features of this wonderful leader, for the generation that is growing up, and for future generations, and also for the hundreds of thousands and maybe even millions of people who will be supremely happy to see the physical features of this person (p. 188).
I’m not arguing that the physical body of Lenin was actually useful as a mobilization device. There is little evidence that people came to the Lenin mausoleum for “spiritual” reasons, or that they experienced great “happiness” upon seeing Lenin – more likely, as Tumarkin argues, they came “out of a combined sense of political duty and fascination, or even morbid curiosity” (
p. 197). But at the end of the day, leading Bolsheviks felt strongly that Lenin’s body needed to be preserved; to
them the physical body of Lenin was inextricably tied to his symbolic and representative function. It became a “fetish” in the
technical Marxist sense of the word.
It is tempting to dismiss these things as the result of sheer “
flattery inflation.” But while flattery inflation was certainly going on (Tumarkin tells some very humorous anecdotes about that), the Bolsheviks still needed to come up with a
theory of representation to justify the veneration of Lenin, whether mostly spontaneous (as in the aftermath of Lenin’s shooting in 1918) or more orchestrated (as in the aftermath of Lenin’s death in 1923). For all the bad faith required (since almost everyone agreed that ruler veneration was a feudal practice that had no place in a Marxist state), this theory remained remarkably consistent from Lenin to Stalin and even beyond Stalin, after Khrushchev denounced the “cult of personality” in the famous “
Secret Speech” to the 20th Party Congress. Even Stalin, whose cult was, to put it somewhat uncharitably, basically a
cynical ploy to concentrate power, felt the need to indicate that the veneration of “Stalin” was not the veneration of the mortal Iosif Vissarionovich Dzhugashvili, but the glorification of the Soviet state. There’s a funny anecdote
Jan Plamper retells in his book on the Stalin cult that shows how seriously Stalin took this idea:
Artyom Sergeev, Stalin’s adopted son, was also fond of telling a story. He recalled a fight between Stalin and his biological son Vasily. After he found out that Vasily had used his famous last name to escape punishment for one of his drunken debauches, Stalin screamed at him. ‘But I’m a Stalin too,’ retorted Vasily. ‘No, you’re not,’ said Stalin. `You’re not Stalin and I’m not Stalin. Stalin is Soviet power. Stalin is what he is in the newspapers and the portraits, not you, not even me! (Plamper, The Stalin Cult, p. xiii)
Stalin could be venerated and respected because “Stalin” did not refer to the king’s mortal body, with all its failings, but to his representative function. To be sure, Stalin’s drive towards “totalization” – to paraphrase
Mussolini, “all within Soviet power, nothing outside Soviet power, nothing against Soviet power” – meant that perhaps unlike Lenin, Stalin had to represent
everything. As Tumarkin puts it, “Lenin was … like a Greek or Roman god who was master in only one field of activity” while “Stalin in the heyday of his personality cult wished to be recognized as superlative in everything - philosophy, linguistics, military strategy - like an omniscient deity” (
p. 60). As the power of the state expanded, so did the domain of charismatic representation.
I suspect a similar theory of representation developed in China after Khrushchev’s denunciation of the cult of personality in Russia prompted some soul-searching about the cult of Mao within the Chinese Communist Party (as I noted
here). In China, the distinction between the “correct” cult of truth (
geren chongbai 个人 崇拜) and the “incorrect” veneration of mere persons (
geren mixin 个人 迷信), however transparently driven by Mao’s desire to concentrate power, remained within the orbit of a (non-Marxist) theory of representation that derived the charismatic claim to authority from the credibility of the leader’s claim to symbolize the truth of the Chinese revolution. And yet, as in Russia, the actual physical body of the ruler mattered; the ruler was never purely an abstract symbol. Mao the
superhuman swimmer,
Mao’s mangoes, Mao’s physical appearance - they were all infused by Mao the truth of the revolution.
Perhaps I’m making too much of this. But it strikes me that the independent Communist reinvention of medieval theories of representation as a way to accommodate “charismatic” claims to authority (real or fake - it doesn’t matter), despite the obvious theoretical inconsistency between leader worship and classical Marxism, is indicative of a broader problematic of modern politics
in a democratic age. Put bluntly, all mass politics is symbolic politics (whether in democratic or non-democratic contexts); and thus what we might call the “charismatic temptation” – the temptation to grant authority to a person who embodies these symbols, rather than to the law, or the constitution – remains ever present.